VRF Systems
Variable Refrigerant Flow (VRF) systems are advanced HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) solutions designed to provide high efficiency, flexibility, and individual comfort control. Commonly used in commercial buildings, offices, hotels, and even large residential complexes, VRF systems are known for their energy efficiency, quiet operation, and zoning capabilities.
Key Features and Benefits of VRF Systems
Energy Efficiency
Variable Speed Compressors: VRF systems utilize variable-speed compressors that adjust the refrigerant flow according to the precise cooling or heating needs of each zone, minimizing energy consumption.
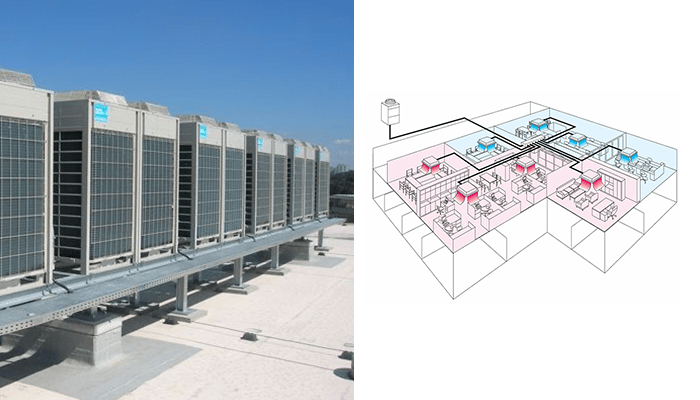
Inverter Technology: The use of inverter-driven compressors allows the system to operate at variable speeds, leading to significant energy savings compared to traditional HVAC systems with fixed-speed compressors.
Heat Recovery: Some VRF systems offer heat recovery capabilities, allowing simultaneous heating and cooling in different zones, which can further enhance energy efficiency.
Zoning Flexibility
Individual Zone Control: VRF systems allow different areas (zones) within a building to be controlled independently. This means each room or zone can have its own temperature setting, providing tailored comfort to occupants.
Wide Range of Indoor Units: VRF systems support a variety of indoor units, including wall-mounted, ceiling cassette, ducted, and floor-mounted units, providing design flexibility for different spaces.
Comfort and Quiet Operation
Precise Temperature Control: The system continuously adjusts the refrigerant flow to maintain the desired indoor temperature with minimal fluctuations, ensuring consistent comfort.
Low Noise Levels: VRF systems operate quietly, as they use multiple smaller indoor units and advanced fan designs, making them suitable for noise-sensitive environments such as offices, hospitals, and residential buildings.
Compact and Space-Saving Design
Smaller Outdoor Units: VRF systems typically have compact outdoor units that require less space compared to traditional chiller systems, making them ideal for buildings with limited exterior space.
Reduced Ductwork: Since VRF systems use smaller refrigerant pipes instead of large air ducts, they reduce the need for extensive ductwork, saving ceiling and wall space.
Ease of Installation and Maintenance
Modular Installation: The modular nature of VRF systems allows for phased installation, making them suitable for both new construction and retrofitting existing buildings.
Simplified Maintenance: VRF systems often come with advanced diagnostics and control systems that allow easy monitoring and maintenance, reducing downtime and repair costs.
Versatility and Scalability
Wide Range of Applications: VRF systems are highly versatile and can be used in a variety of settings, from small apartments to large commercial buildings.
Scalable Design: They can be easily scaled up or down to match the cooling and heating requirements of the space, offering flexibility for future expansions.
Types of VRF Systems
Heat Pump VRF Systems
Single Mode Operation: These systems provide either cooling or heating at any given time across the entire system, making them suitable for open-plan offices or large areas with similar heating/cooling needs.
Heat Recovery VRF Systems
Simultaneous Heating and Cooling: These systems can simultaneously provide cooling and heating to different zones, which is ideal for buildings with varying thermal requirements, such as hotels, hospitals, and multi-use buildings.
Energy Efficiency: Heat recovery systems use waste heat from cooling processes to provide heating, enhancing overall energy efficiency.
Considerations for Selecting a VRF System
Building Size and Layout
Consider the building’s size, layout, and number of zones to determine the type and capacity of the VRF system required.
Energy Efficiency Goals
Look for VRF systems with high energy efficiency ratings (such as SEER and EER) and advanced features like heat recovery to maximize energy savings.
Installation and Maintenance Costs
Evaluate the initial cost of the system, installation complexity, and ongoing maintenance requirements to ensure a cost-effective solution.
Compatibility with Building Management Systems (BMS)
Ensure that the VRF system is compatible with existing or planned building management systems for seamless integration and control.
Local Climate Conditions
Consider the local climate and specific heating and cooling needs to choose the appropriate VRF model.


